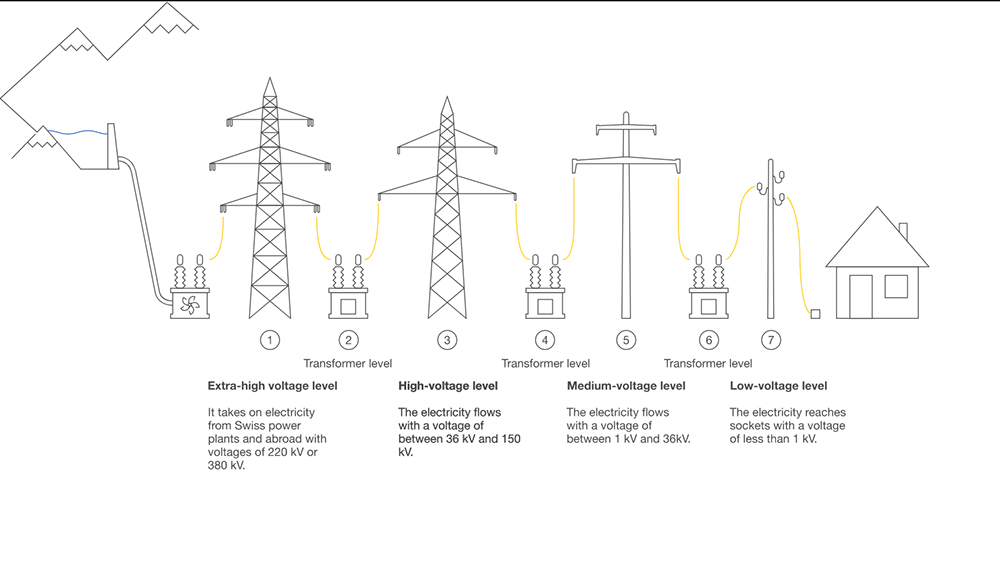
In Vietnam’s power transmission regulation 1993 on the content “Reactive power compensation for electricity supply and distribution grid”, there are 3 voltage levels including:
- Low voltage with rated voltage up to 1kV;
- Medium voltage with rated voltage up to 36kV. Specifying specific norms such as 6kV, 10kV, 15kV, 22kV, 35kV;
- High-voltage electricity with a nominal voltage of 36kV or more. Specify specific norms such as 66kV, 110kV, 220kV, 500kV.
I. Low voltage electricity
Low voltage electricity is the power supply with transmission voltage up to 1kV. Low-voltage cables are used to transmit electricity for civil power networks and industrial projects, factories, apartments, offices, hospitals, etc.
This voltage level does not cause discharge when standing close, but can still be dangerous to life if it touches the load core directly. That is why civil wires, low voltage cables are required to have the following insulation and sheath:
1. TCVN 6610-3: 2000
- Single-core unsheathed cable with solid conductor and conductor temperature of 70°C for internal installation (6610 TCVN 05 or 227 IEC 05);
- Single-core unsheathed cable with flexible conductor and conductor temperature of 70 degrees Celsius for internal installation (6610 TCVN 06 or 227 IEC 06);
2. TCVN 6610-5: 2014 (PVC insulated flexible wire)
- Flat tinsel wire (6610 TCVN 41/60227 IEC 41);
- Flexible cord for indoor decorative lighting (6610 TCVN 43/60227 IEC 43);
- Light PVC sheathed wire (6610 TCVN 52/60227 IEC 52);
- General purpose PVC sheathed flexible cord (6610 TCVN 53 or 60227 IEC 53);
- Heat-resistant lightweight PVC sheathed flexible wire for conductors with a maximum temperature of 90 degrees Celsius (6610 TCVN 56 or 60227 IEC 56);
- Heat-resistant ordinary PVC sheathed flexible wire for conductors with a maximum temperature of 90 degrees Celsius (6610 TCVN 57 or 60227 IEC 57).
3. TCVN 5935-1:2013: Cable used to transmit voltage up to 0.6/1kV
- Nominal voltage 0.6/1 (1.2) kV;
- Insulating compound
- PVC thermoplastic;
- Cross-linked insulating compound: Ethylene propylene rubber or the like (EPR), molecular rubber or high hardness ethylene propylene rubber (HEPR), Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE).
- The maximum conductor temperature in normal operation is 70 degrees C (if PVC insulation) and 90 degrees C (if XLPE insulation).
- Conductors: Must be class 1 (1 solid conductor) or class 2 (braided conductor) (according to IEC 60228:2004) of annealed copper/coated with aluminum or aluminum alloy.
II. Medium voltage electricity
Medium voltage is the power supply with transmission voltage up to 36kV. Medium voltage cables are used to transmit electricity to this power network.
Medium voltage power cables are specified according to TCVN 5935-1: 2013 and TCVN 5935-2: 2013 with the following basic contents:
TCVN 5935-2:2013 – Part 2
Cables for rated voltages from 6 kV (Um = 7.2 kV) to 30 kV (Um = 36 kV).
- The rated voltage Uo/U(Um) of the cables considered in this standard is as follows: Uo/U(Um) = 3.6/6 (7.2) – 6/10 (12) – 8.7 /15 (17.5) – 12/20 (24) – 18/10 (36) kV.
- Insulating compound
- PVC/B for cable lines with rated voltage Uo/U = 3.6/6 kV;
- Thermosetting plastic: Ethylene propylene rubber or similar (EPR), High hardness ethylene propylene rubber or rubber (HEPR), Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE);
- Maximum conductor temperature in normal operation: For PVC/B it is 70 degrees Celsius, for EPR/ HEPR/ XLPE it is 90 degrees Celsius.
- Conductors: shall be class 1 (1 solid conductor) or class 2 (braided conductor) of metallized annealed copper with aluminum/aluminum alloy in accordance with IEC 60228.
- Specifies the nominal thickness of insulation layers PVC/B, XLPE, EPR/HEPR;
- Specifications for three-core cable assemblies, inner sheaths and fillers.
Safe distance of overhead power lines
Medium voltage is a dangerous voltage level, which can cause discharge when standing close, so the high voltage safety protection corridor is very clearly specified in Decree 14/2014/ND-CP as follows:
Corridor width (limited by two vertical faces on either side of the line, parallel to the line, with a distance from the outermost wire to each side when the line is stationary):
- Voltage up to 35kV, minimum distance is 1.5m for shielded wire and 3m for bare wire;
- Voltage up to 22kV, minimum distance is 1m for shielded wire and 2m for bare wire.
Corridor height (from the bottom of the column foundation to the highest point of the building plus the vertical safety distance): Voltage up to 35kV, the minimum distance is 2m.
The safety corridor of electric cables traveling on the ground or suspended in the air must be limited to 0.5 m from all sides from the outer surface of the outermost cable.
Subway safety distance
The width of the corridor (two vertical sides away from the outer surface of the cable sheath or the outermost cable on both sides of the underground electric cable for cables placed directly in the ground) is specified as follows:
- Minimum distance of 1m for cables laid directly in stable land, 1.5m in unstable land;
- The minimum distance is 20m for cables placed in the water and in places where there are no ships passing, at least 100m in places where there are ships passing by.
Identify medium voltage lines
Medium voltage electricity uses concrete poles ~10 – 15m high to transmit electricity.
III. High voltage electricity
Low voltage electricity is the power supply with transmission voltage from 36kV. This voltage level is used to transmit electricity from national power generation plants to regional or provincial transfer stations, then through low voltage substations and transmit to civil works.
Safe distance
High-voltage cables are regulated according to the standard TCVN 12227:2018. High voltage electricity is especially dangerous to humans, the safety protection corridor is specified in Decree 14/2014/ND-CP as follows:
Corridor width (limited by two vertical sides on both sides of the line, parallel to the line, with a distance from the outermost wire to each side when the line is in a static state): Voltage from 110kV, approx. Minimum distance is 4m.
Corridor height (calculated from the bottom of the column foundation to the highest point of the building plus the vertical safety distance): Voltage from 110kV, the minimum distance is 3m.
Identify high voltage power lines
High-voltage power lines are transmitted through steel poles or towers, with a minimum height of 30-40m above the ground.