Insulation standards of electric cables are specified in Vietnamese standards on production and quality testing of cables, the purpose is to ensure normal and safe operation of the power network.
That standard is clearly expressed in: TCVN 6610 for civil wires and flexible cables, TCVN 5935-1:2013 for low-voltage cables, TCVN 5935-2:2013 for medium-voltage cables, TCVN 6447:1998 for twisted cable. The content of insulation requirements for each product group is as follows:
Insulation standards of medium voltage cables
According to TVCN 5935-2:2013, standards for insulation of medium voltage cables from 1kV to 36kV are specified as follows:
The types of insulating compounds covered by this standard are listed in the Table below with abbreviated designations.
1. Medium voltage cable insulation compound
| Insulating compound | Shortened symbol |
| a) ThermoplasticsPolyvinyl chloride is used for cables with rated voltage Uo/U = 3.6/6 kV | PVC/B* |
| b) Heat hard plasticEthylene propylene rubber or the like (EPM or EPDM)
Molecular rubber or high hardness ethylene propylene rubber Cross-linked polyethylene |
EPR
HEPR XLPE |
| * Polyvinyl chloride-based insulating compounds used for cables with rated voltage Uo/U ≤ 1.8/3 kV are denoted PVC/A in IEC 60502-1. | |
The highest conductor temperatures for the different types of insulating compounds covered by this standard are given in the table below.
| Insulating compound | Highest conductor temperature (degrees Celsius) | ||
| Work as usual | Short circuit(longest time is 5s) | ||
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC/B )
Cross-linked Polyethylene (XLPE) Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR and HEPR) |
70
70 90 90 |
160
140 250 250 |
|
2. Medium voltage cable insulation thickness
The nominal insulation thicknesses are specified in the following 3 tables.
The thickness of any separator or semiconductor screen on the conductor or outside the insulation is not included in the insulation thickness.
Table – Nominal thickness of PVC/B insulation
| Nominal cross-sectional area of conductormm2 | Nominal thickness of insulation at rated voltage 3.6/6 (7.2) kVmm |
| 10 to 1 600 | 3.4 |
| NOTE 1 Conductors with a cross-sectional area less than that given in this table should not be used. However, if a smaller cross-section is required, the conductor diameter can be increased by means of a conductor screen (see 7.1) or the insulation thickness can be increased to limit the maximum electrical stresses applied to the insulation. under the test voltage at the values calculated with the smallest conductor sizes given in this table.NOTE 2 For conductors with cross-sections greater than 1 000 mm2, the insulation thickness can be increased to avoid mechanical damage during installation and service. | |
Table – Nominal thickness of cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulation
| Nominal cross-sectional area of conductormm2 | Nominal thickness of insulation at rated voltage Uo/U(Um) | ||||
| 3.6/6 (7.2) kVmm | 6/10 (12) kVmm | 8.7/15 (17.5) kVmm | 12/20 (24) kVmm | 18/30 (36) kVmm | |
| ten16
25 35 50 to 185 240 300 400 500 to 1600 |
2.52.5
2.5 2.5 2.5 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 |
–3.4
3.4 3.4 3.4 3.4 3.4 3.4 3.4 |
––
4.5 4.5 4.5 4.5 4.5 4.5 4.5 |
––
– 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5 |
––
– – 8.0 8.0 8.0 8.0 8.0 |
| NOTE 1 Conductors with a cross-sectional area less than that given in this table should not be used. However, if a smaller cross-section is required, the conductor diameter can be increased by means of a conductor screen (see 7.1) or the insulation thickness can be increased to limit the maximum electrical stresses applied to the insulation. under the test voltage at the values calculated with the smallest conductor sizes given in this table.NOTE 2 For conductors with cross-sections greater than 1 000 mm2, the insulation thickness can be increased to avoid mechanical damage during installation and service. | |||||
Table – Nominal thickness of ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) insulation and hard ethylene propylene rubber (HEPR) insulation
| Nominal cross-sectional area of conductormm2 | Nominal thickness of insulation at rated voltage Uo/U(Um) | |||||
| 3.6/6 (7,2)kV | 6/10 (12)kV | 8.7/15 (17.5)kV | 12/20 (24)kV | 18/30 (36)kV | ||
| There is no barriermm | There is a curtainmm | mm | mm | mm | mm | |
| ten16
25 35 50 to 185 240 300 400 500 to 1 600 |
3.03.0
3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.2 |
2.52.5
2.5 2.5 2.5 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 |
–3.4
3.4 3.4 3.4 3.4 3.4 3.4 3.4 |
––
4.5 4.5 4.5 4.5 4.5 4.5 4.5 |
––
– 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5 |
––
– – 8.0 8.0 8.0 8.0 8.0 |
| NOTE 1 Conductors with a cross-sectional area less than that given in this table should not be used. However, if a smaller cross-section is required, the conductor diameter can be increased by means of a conductor screen (see 7.1) or the insulation thickness can be increased to limit the maximum electrical stresses applied to the insulation. under the test voltage at the values calculated with the smallest conductor sizes given in this table.NOTE 2 For conductors with cross-sections greater than 1 000 mm2, the insulation thickness can be increased to avoid mechanical damage during installation and service. | ||||||
Insulation standards of low voltage cables
According to TVCN 5935-1:2013, standards for insulation of low voltage cables up to 1kV are specified as follows:
1. Insulating compound
The types of insulating compounds covered by this standard are listed in the Table below with abbreviated designations.
Table – Insulating compounds
| Insulating compound | Shortened symbol |
| a) Thermoplastics.Polyvinyl chloride is used for cables with rated voltage Uo/U £1.8/3 kV | PVC/A* |
| b) Horizontal linkEthylene propylene rubber or the like (EPM or EPDM)
Molecular rubber or ethylene propylene rubber with high hardness Cross-linked polyethylene |
EPR
HEPR XLPE |
| * Polyvinyl chloride based insulating compounds used for cables with rated voltage Uo/U = 3.6/6 kV are denoted PVC/B in IEC 60502-2. | |
2. Insulation thickness
| Nominal cross-sectional area of conductor mm2 |
Nominal thickness of insulation at rated voltage Uo/U (Um) |
|
| 0.6/1 (1.2) kV mm2 |
1.8/3 (3.6) kV mm2 |
|
| 1.5 and 2.54 and 6
10 and 16 25 and 35 50 and 70 95 and 120 150 185 240 300 400 500 to 800 1 000 won |
0.81.0
1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 |
––
2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 |
| NOTE It is not recommended to use conductors with cross-sections less than the values given in this table. | ||
Table – Nominal thickness of cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulation
| Nominal cross-sectional area of conductor mm2 |
Nominal thickness of insulation at rated voltage Uo/U (Um) |
||
| 0.6/1 (1.2) kV mm2 |
1.8/3 (3.6) kV mm2 |
||
| 1.5 and 2.54 and 6
10 and 16 25 and 35 50 70 and 95 120 150 185 240 300 400 500 630 800 1 000 won |
0.70.7
0.7 0.9 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.7 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 |
––
2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 |
|
| NOTE It is not recommended to use conductors with cross-sections less than the values given in this table. | |||
Table – Nominal thickness of ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) insulation and hard ethylene propylene rubber (HEPR) insulation
| Nominal cross-sectional area of conductor mm2 |
Nominal thickness of insulation at rated voltage Uo/U (Um) |
|||
| 0.6/1 (1.2) kV mm2 |
1.8/3 (3.6) kV mm2 |
|||
| EPRmm | HEPRmm | EPRmm | HEPRmm | |
| 1.5 and 2.54 and 6
10 and 16 25 and 35 50 70 95 120 150 185 240 300 400 500 630 800 1 000 won |
1.01.0
1.0 1.2 1.4 1.4 1.6 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 2.8 2.8 3.0 |
0.70.7
0.7 0.9 1.0 1.1 1.1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.7 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 |
––
2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.4 2.4 2.4 2.4 2.4 2.4 2.6 2.8 2.8 2.8 3.0 |
––
2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 |
| NOTE It is not recommended to use conductors with cross-sections less than the values given in this table. | ||||
Insulation standards of twisted-pair cables
1. Requirements for insulation
Insulation shall be made of XLPE material having an ash content of not less than 2% by mass. Insulation shall be uniform, firmly adhered to the conductor but still able to be separated from the conductor, and comply with tables 1 and 2 of this standard.
The insulation of twisted-pair cables can be XLPE, symbol X-90 or special XLPE with higher heat resistance, symbol X-FP-90.
2. Insulation thickness
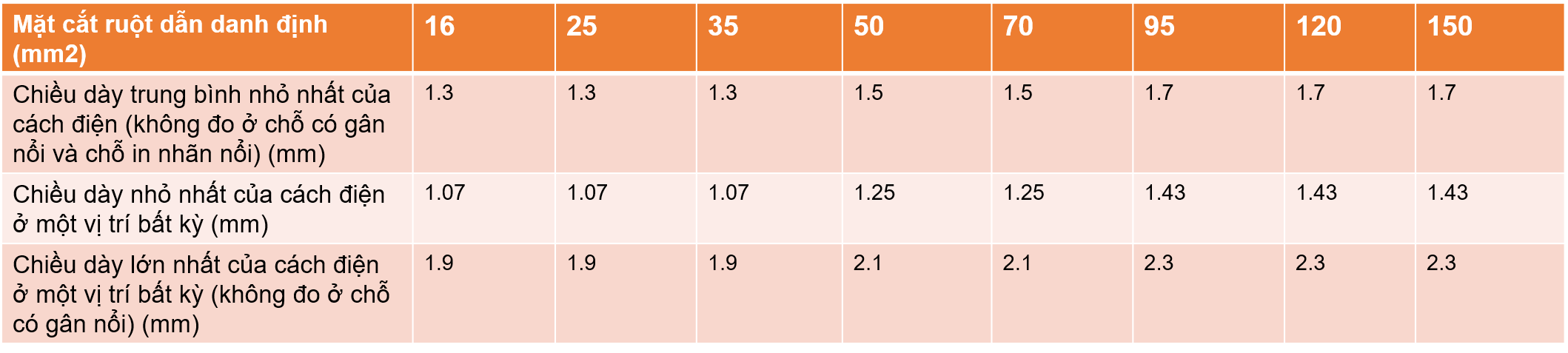
Insulation standards of civil electrical wires , flexible cables
1. TCVN 6610-3:2000
- Single-core unsheathed cable with solid conductor and conductor temperature of 70 degrees Celsius for internal installation (6610 TCVN 05 or 227 IEC 05): Rated voltage up to 300/500V, number of conductors 1 and class 1 conductors (solid conductor 1 solid wire), PVC/C insulation thickness from 0.6mm;
- Single-core unsheathed cable with flexible conductor and conductor temperature of 70 degrees Celsius for internal installation (6610 TCVN 06 or 227 IEC 06): Rated voltage up to 300/500V, number of conductors 1 and grade 5 conductors (soft conductors), PVC/C insulation thickness from 0.6mm.
2. TCVN 6610-5: 2014
- Flat tinsel wire (6610 TCVN 41/60227 IEC 41): Nominal voltage 300/300V, 2 conductors, insulation thickness PVC or PVC/D 0.8mm;
- Flexible cord for indoor decorative lighting (6610 TCVN 43/60227 IEC 43): Rated voltage 300/300V, number of class 1 and class 6 conductors (softer than class 5 conductors), insulation thickness power PVC or PVC/D medium 0.7mm;
- Light PVC sheathed wire (6610 TCVN 52/60227 IEC 52): Rated voltage 300/300V, 2 and 3 class 5 conductors (soft conductors), average 0.5mm PVC or PVC/D insulation;
- Common PVC sheathed flexible cord (6610 TCVN 53 or 60227 IEC 53): Rated voltage 300/500V, number of conductors from 2 to 5 and class 5 conductors, average PVC or PVC/D insulation from 0.6mm;
- Flexible wire with light PVC sheathed heat resistant for conductors with a maximum temperature of 90 degrees Celsius (6610 TCVN 56 or 60227 IEC 56): Rated voltage 300/300V, number of conductors from 2 to 3 and conductors grade 5 conductor, average 0.5mm PVC or PVC/E insulation;
- Heat-resistant ordinary PVC sheathed flexible wire for conductors with a maximum temperature of 90 degrees Celsius (6610 TCVN 57 or 60227 IEC 57): Rated voltage 300/500V, number of conductors from 2 to 5 and conductors grade 5 conductor, average 0.6mm PVC or PVC/E insulation.

