The conductor cross-section is the cross-sectional area of the conductive core. The cross-section must be perpendicular to the axis of the conductor, and since the conductive core is usually cylindrical, the cross-section of the main conductor is equal to the circular cross-sectional area of the core.
Thus, conductor cross-section = S = π.RR where R is the circular cross-sectional radius of the conductor core.
Based on actual conditions, the conductor cross-section must be calculated based on the power used by the electrical equipment or the amperage that the wire can carry.
The formula for calculating the cross-sectional area of a conductor is as follows:
S = I / J (kt) = P / J (kt). U. In which:
- P is power consumed by electrical equipment (W);
- U is the potential difference between the two conductors (V);
- I is the amperage (A);
- J(kt) is the economic current density (A/mm2).
In addition to calculating the conductor cross-section according to economic current density, there are also two other methods including the calculation of the cross-section based on the allowable voltage loss, the calculation of the cross-section based on the allowable heating, based on the corona condition. . All four methods are specified in Decision 19/2006-BCN.
Conductor cross-section lookup table
The conductor cross-sectional lookup table is also regulated according to the industry standard on electrical transmission system 11TCN 19/2006 in Decision 19/2006/BCN. The following content:
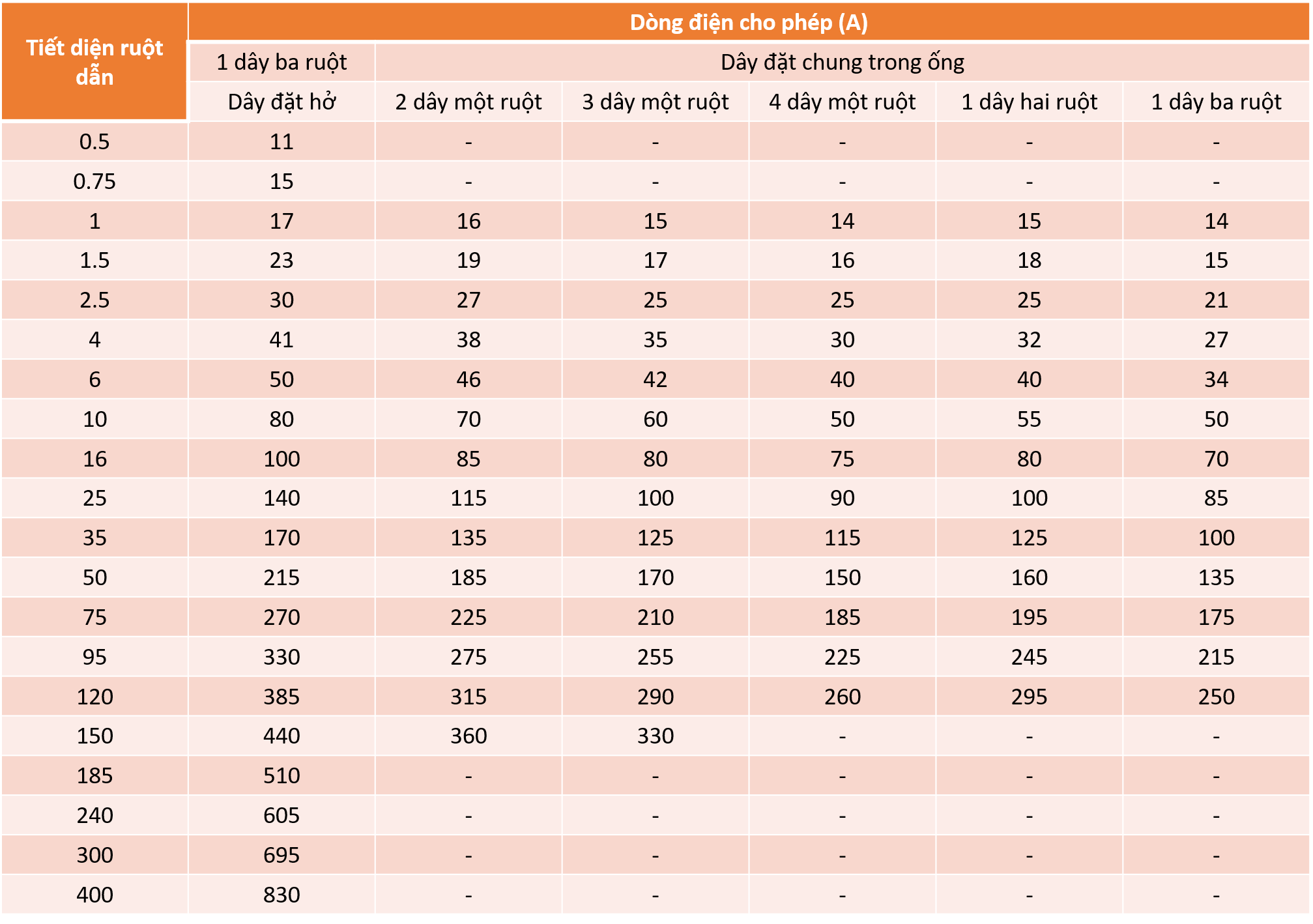
Permissible long-term current of rubber- or PVC-coated copper conductor low-voltage conductors
Permissible long-term current of low-voltage copper conductors, rubber-insulated copper conductors with metal shielding, and rubber-insulated copper conductors in lead, PVC or rubber sheaths with or without steel belts
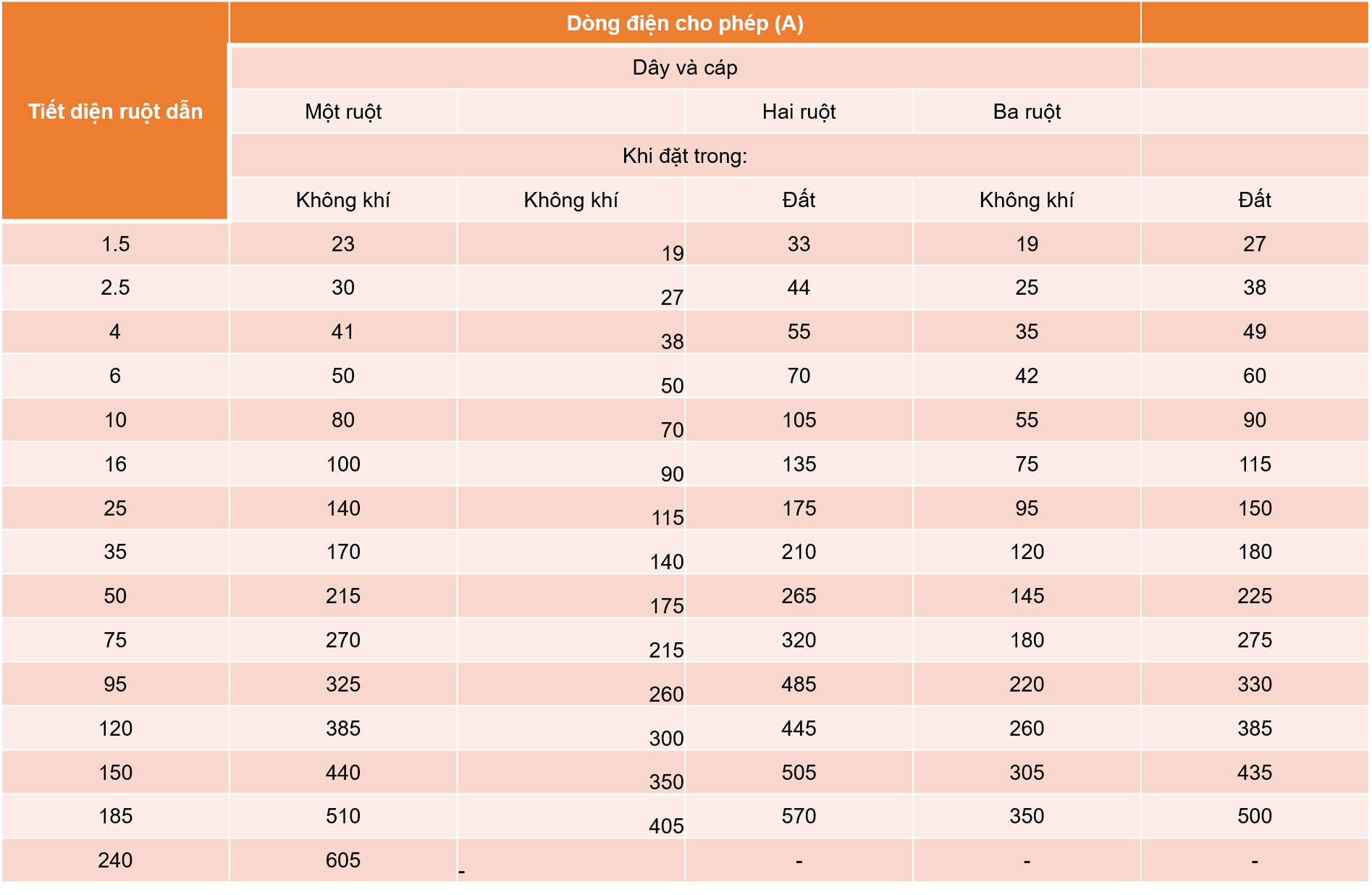
Permissible long-term current of rubber-insulated aluminum or PVC-insulated low-voltage conductors

Permissible long-term current of rubber or plastic-insulated aluminum low-voltage cables with metal, PVC or rubber protective sheath, with or without steel belt

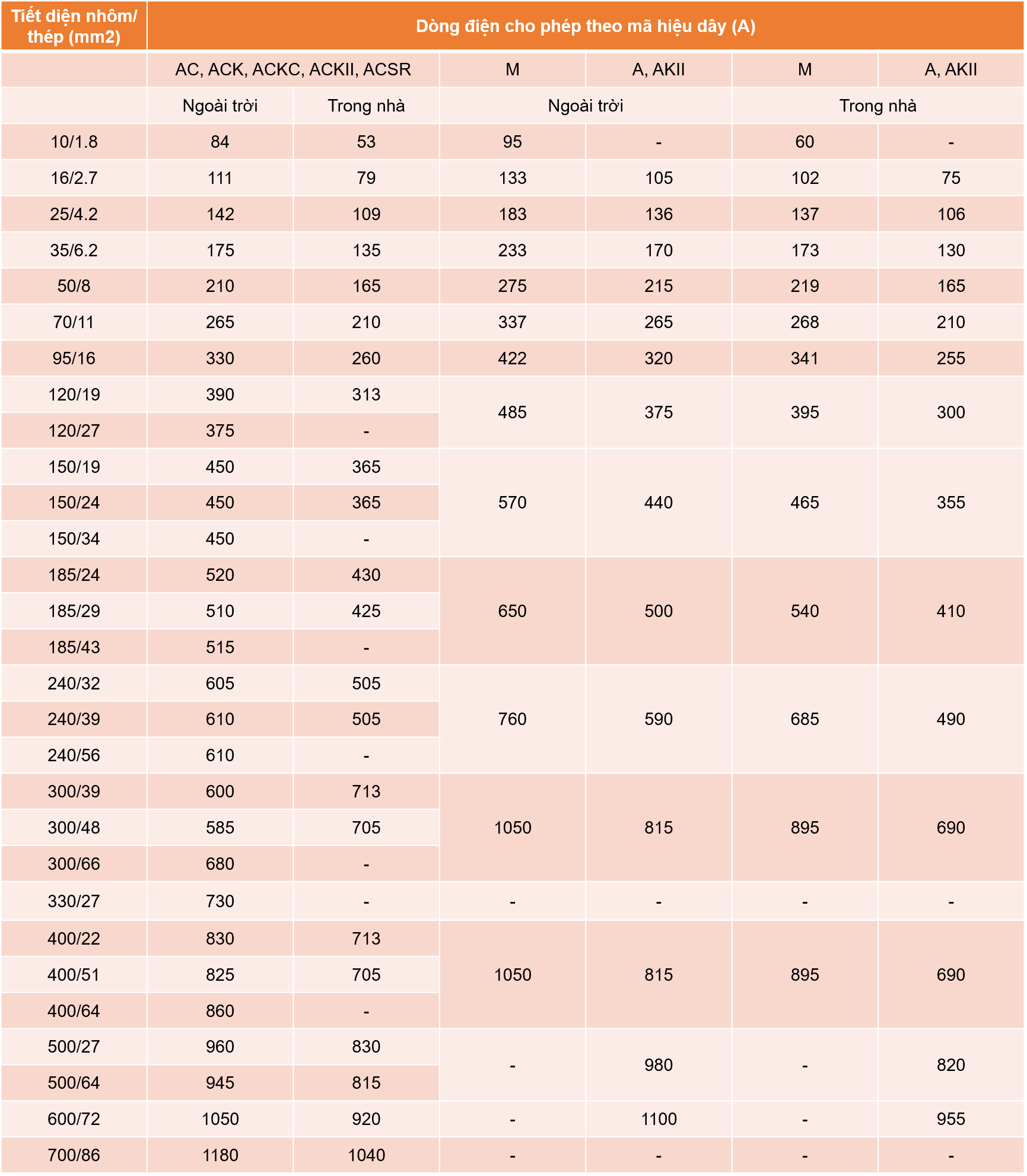
Permissible long-term current according to the heat emission of bare copper, aluminum or steel-cored wires (allowable heating is +70°C, when the air temperature is 25°C)
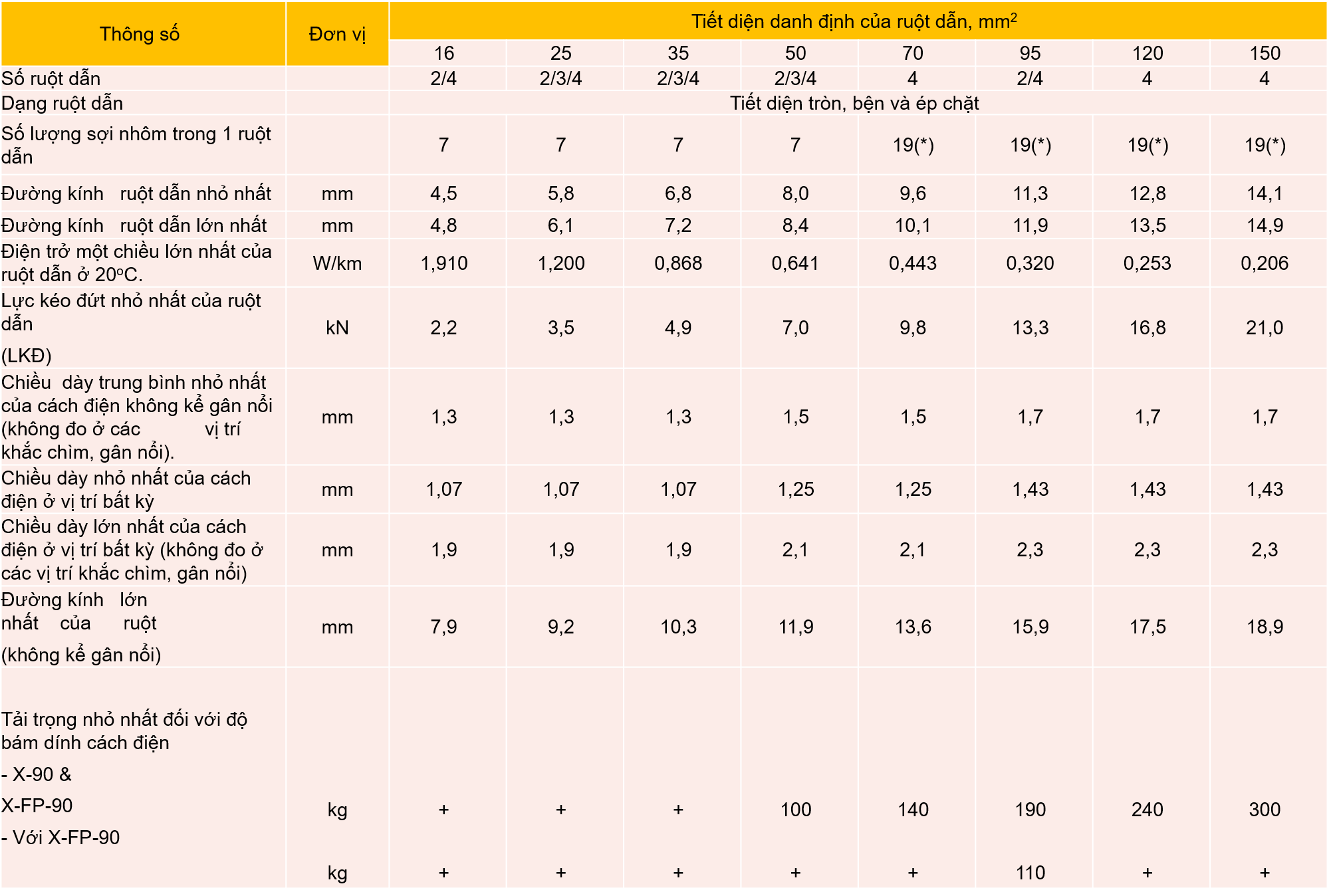
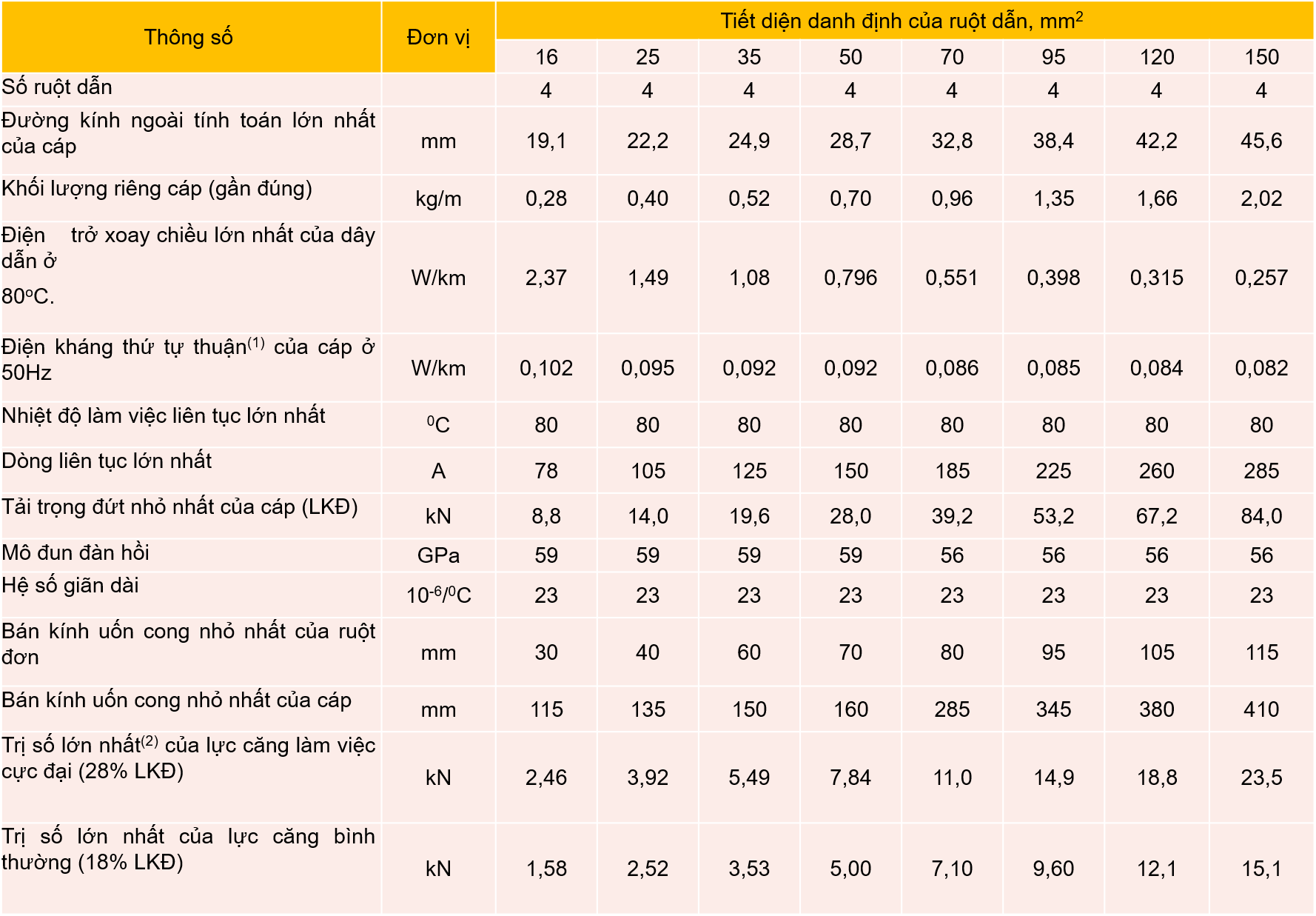
Specifications of 4-core, aluminum-core cable
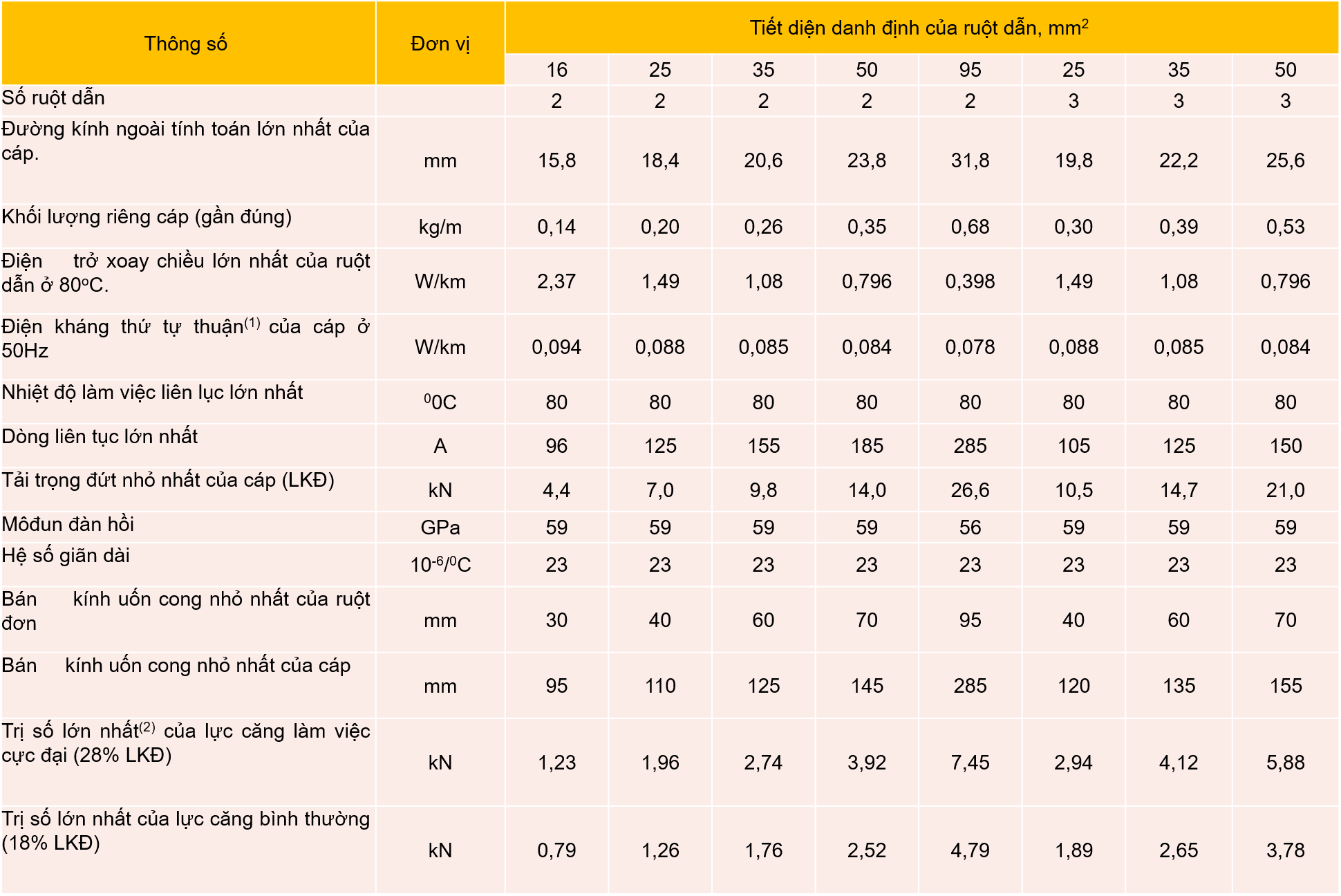
Specifications for 2- and 3-core cables, aluminum cores
Specifications of aluminum twisted-pair cable with uniform load