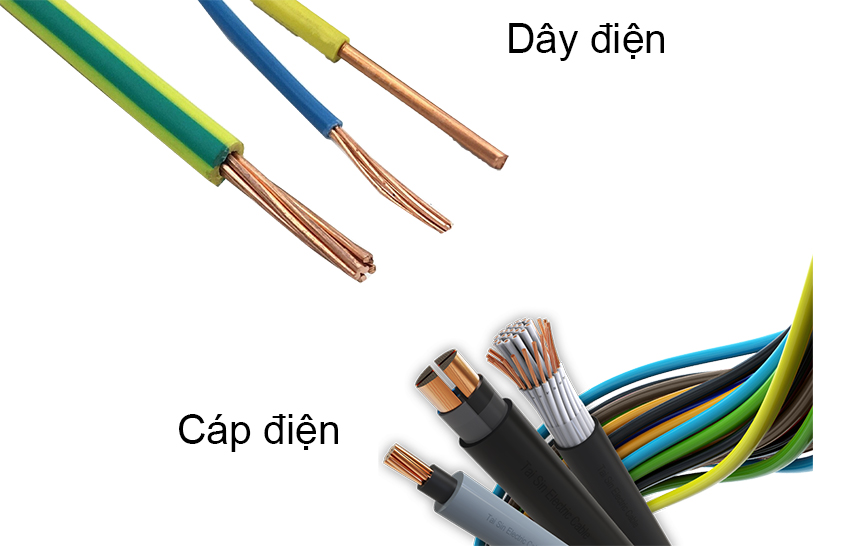
The scope of this article is within the framework of electrical conductors and cables, used to transmit electricity.
Wire
Electric wires are conductor lines used to transmit electricity for civil power networks up to 750V, including 1-core and more than 1-core wires (from 2 to 5 conductors or more at the request of customers). . Conductive cores are manufactured using conductive materials, usually copper or aluminum.
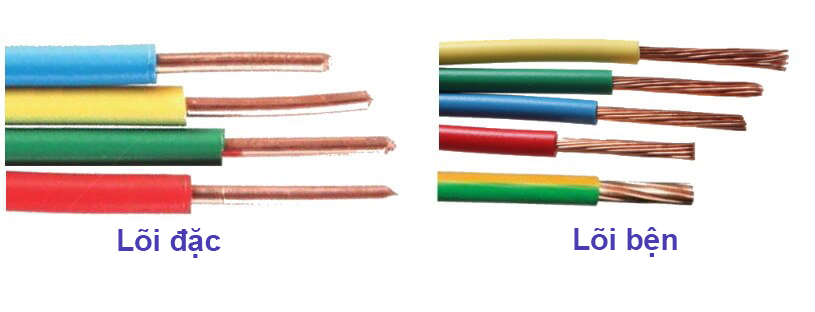
- For wires with 1 core: The conductor can be in the form of 1 hard wire or many soft wires as shown in the image below;
- For electric wires with 2 or more cores: The conductive core consists of many twisted and twisted soft wires.
The conductive core of the wire is covered with an insulating layer, mainly of PVC. For wires with 2 cores or more, the outer sheath is also made of PVC.
Most power lines are used to transmit voltages up to 300/500V, single-core rigid wire can carry voltages up to 450/750V. Single-core hard-wired wires have low resistance for better power transmission, while wires using braided cores have higher strength.
Electric cable
Power cables are used to transmit voltages of 1kV or more, power cables also have 1 or more conductor cores, but the core structure and insulation layer are more complicated.
In particular, 2 products of 1-core soft power cable, which is a PVC-coated 450/750V 1-core soft aluminum cable and a PVC-coated 1-core 450/750V soft copper cable, are used to transmit voltages to the power network up to 750V. (civil and industrial electricity).
The basic structure of the power cable includes:
- Conductive core consisting of many copper/aluminum/aluminum filaments + twisted-twisted technical round galvanized steel wire;
- Conductive core with insulation, usually XLPE ;
- The insulation and core are covered with a protective sheath.
Some special power cables such as underground cables or fireproof cables will have additional layers of screens or semiconductor layers between the upper layers to ensure actual and safe operation standards.